Microsoft Lan Manager
Applies to
- Feb 22, 2013 LAN-MANAGER is an application which will be able to monitor networks,to analyze the network's topology and warn the network's administrator in case of an incident.
- Nov 07, 2017 LAN Manager is the ' grandpa of authentication ' in Windows Systems. It was implemented in 1987 and nowadays it is old and deprecated. And yes of course, it can be broken easily. This protocol is still used by Windows-NT based operating systems to store Password Hashes.
- Apr 19, 2017 The LAN Manager hash is relatively weak and prone to attack compared to the cryptographically stronger NTLM hash. Because the LM hash is stored on the local device in the security database, the passwords can be compromised if the security database, Security Accounts Manager (SAM), is attacked.
- May 27, 2015 Although, for the most part, setting up a wired network connection on a Windows 10 device is as easy as plugging in an Ethernet cable, connecting using a.
- Apr 19, 2017 LAN Manager (LM) includes client computer and server software from Microsoft that allows users to link personal devices together on a single network. Network capabilities include transparent file and print sharing, user security features, and network administration tools.
- Windows 10
Describes the best practices, location, values, policy management and security considerations for the Network security: LAN Manager authentication level security policy setting.
(1) An earlier network operating system from Microsoft that ran as a server application under OS/2. Supporting DOS, Windows and OS/2 clients, LAN Manager was superseded by Windows NT Server, and parts of LAN Manager were used in Windows NT and 2000. See LAN Server. (2) (Local Area Network manager) See network administrator.
Reference
This policy setting determines which challenge or response authentication protocol is used for network logons. LAN Manager (LM) includes client computer and server software from Microsoft that allows users to link personal devices together on a single network. Network capabilities include transparent file and print sharing, user security features, and network administration tools. In Active Directory domains, the Kerberos protocol is the default authentication protocol. However, if the Kerberos protocol is not negotiated for some reason, Active Directory uses LM, NTLM, or NTLM version 2 (NTLMv2).
LAN Manager authentication includes the LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 variants, and it is the protocol that is used to authenticate all client devices running the Windows operating system when they perform the following operations:
- Join a domain
- Authenticate between Active Directory forests
- Authenticate to domains based on earlier versions of the Windows operating system
- Authenticate to computers that do not run Windows operating systems, beginning with Windows 2000
- Authenticate to computers that are not in the domain
Possible values
- Send LM & NTLM responses
- Send LM & NTLM - use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated
- Send NTLM responses only
- Send NTLMv2 responses only
- Send NTLMv2 responses only. Refuse LM
- Send NTLMv2 responses only. Refuse LM & NTLM
- Not Defined
The Network security: LAN Manager authentication level setting determines which challenge/response authentication protocol is used for network logons. This choice affects the authentication protocol level that clients use, the session security level that the computers negotiate, and theauthentication level that servers accept. The following table identifies the policy settings, describes the setting, and identifies the security level used in the corresponding registry setting if you choose to use the registry to control this setting instead of the policy setting.
| Setting | Description | Registry security level |
|---|---|---|
| Send LM & NTLM responses | Client devices use LM and NTLM authentication, and they never use NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication. | 0 |
| Send LM & NTLM – use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated | Client devices use LM and NTLM authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication. | 1 |
| Send NTLM response only | Client devices use NTLMv1 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication. | 2 |
| Send NTLMv2 response only | Client devices use NTLMv2 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication. | 3 |
| Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM | Client devices use NTLMv2 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers refuse to accept LM authentication, and they will accept only NTLM and NTLMv2 authentication. | 4 |
| Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM & NTLM | Client devices use NTLMv2 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers refuse to accept LM and NTLM authentication, and they will accept only NTLMv2 authentication. | 5 |
Best practices
- Best practices are dependent on your specific security and authentication requirements.
Policy Location
Computer ConfigurationWindows SettingsSecurity SettingsLocal PoliciesSecurity Options
Registry Location
HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetControlLsaLmCompatibilityLevel
Default values
The following table lists the actual and effective default values for this policy. Default values are also listed on the policy’s property page.
| Server type or GPO | Default value |
|---|---|
| Default Domain Policy | Not defined |
| Default Domain Controller Policy | Not defined |
| Stand-Alone Server Default Settings | Send NTLMv2 response only |
| DC Effective Default Settings | Send NTLMv2 response only |
| Member Server Effective Default Settings | Send NTLMv2 response only |
| Client Computer Effective Default Settings | Not defined |
Policy management
This section describes features and tools that are available to help you manage this policy.
Restart requirement
None. Changes to this policy become effective without a device restart when they are saved locally or distributed through Group Policy.
Group Policy
Modifying this setting may affect compatibility with client devices, services, and applications.
Security considerations
This section describes how an attacker might exploit a feature or its configuration, how to implement the countermeasure, and the possible negative consequences of countermeasure implementation.
Lan Manager Download
Vulnerability
In Windows 7 and Windows Vista, this setting is undefined. In Windows Server 2008 R2 and later, this setting is configured to Send NTLMv2 responses only.
Countermeasure
Configure the Network security: LAN Manager Authentication Level setting to Send NTLMv2 responses only. Microsoft and a number of independent organizations strongly recommend this level of authentication when all client computers support NTLMv2.
Potential impact
Client devices that do not support NTLMv2 authentication cannot authenticate in the domain and access domain resources by using LM and NTLM.
You may want all of the most popular programs in a MicrosoftOffice software package, including Word®, Excel®, PowerPoint® andOneNote®. Raster to vector freeware. If you run a business, you can opt for an Office softwarepackage licensed for business use, which includes these programs as wellas Outlook®.
Related topics
(redirected from Microsoft LAN Manager)Lan Manager
(operating system)LAN Manager
(1) An earlier network operating system from Microsoft that ran as a server application under OS/2. Supporting DOS, Windows and OS/2 clients, LAN Manager was superseded by Windows NT Server, and parts of LAN Manager were used in Windows NT and 2000. See LAN Server.(2)
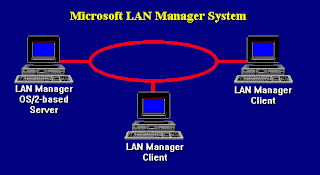 (Local Area Network manager) See network administrator.
(Local Area Network manager) See network administrator.Microsoft Lan Manager 2.2 Download
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.Link to this page:
